Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate nearly every function in the female body — from metabolism and mood to reproduction and energy levels. When these hormones become unbalanced, even slightly, women can experience a wide range of symptoms that affect their physical, emotional, and mental well-being.
- 1. Irregular or Missed Periods
- 2. Unexplained Weight Gain or Loss
- 3. Chronic Fatigue and Low Energy
- 4. Mood Swings and Anxiety
- 5. Sleep Problems
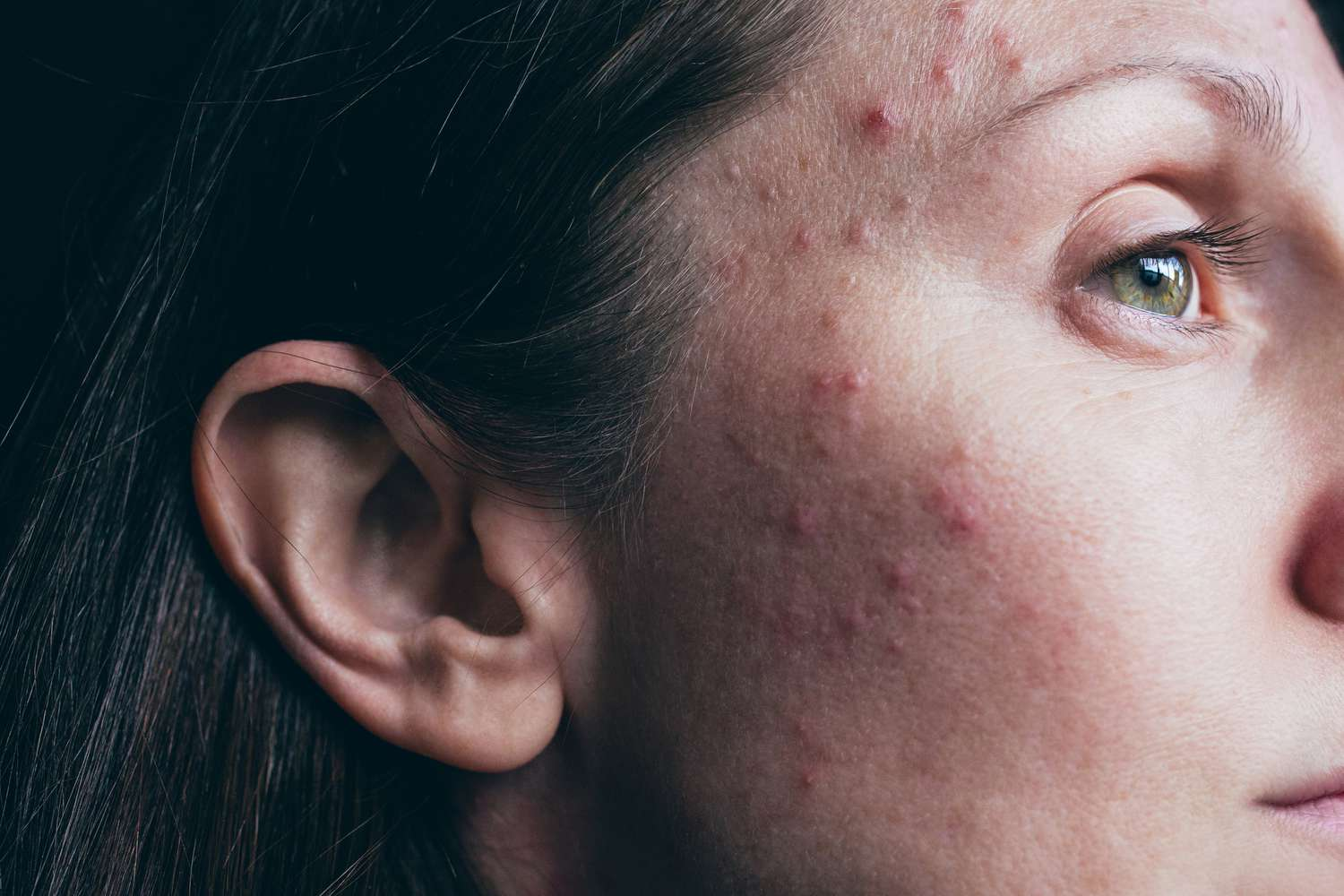
- 6. Acne and Skin Changes
- 7. Hair Thinning or Hair Loss
- 8. Digestive Issues
- 9. Hot Flashes and Night Sweats
- 10. Low Libido
- 11. Memory Issues and Brain Fog
- 12. Breast Tenderness or Changes
- When to See a Doctor
- Final Thoughts
Hormonal imbalances are more common than most women realize and can occur due to stress, poor diet, medical conditions, or natural life stages such as puberty, pregnancy, perimenopause, and menopause. Understanding the common symptoms of hormonal imbalance is the first step toward seeking treatment and restoring health.
1. Irregular or Missed Periods
One of the most noticeable signs of hormonal imbalance is a change in your menstrual cycle.
- Too frequent periods (less than 21 days apart)
- Skipped or missed periods without pregnancy
- Heavy or very light bleeding
- Painful cramps or clotting
These issues may indicate imbalances in estrogen, progesterone, or other reproductive hormones such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
2. Unexplained Weight Gain or Loss
Hormones directly influence metabolism, appetite, and fat storage. If you experience:
- Sudden weight gain despite no change in diet
- Difficulty losing weight, especially around the belly
- Unexplained weight loss with fatigue
…it may be linked to thyroid hormone imbalances, insulin resistance, or cortisol (the stress hormone) issues.
3. Chronic Fatigue and Low Energy
Feeling constantly tired, even after a good night’s sleep, is a common red flag. Low thyroid hormones (hypothyroidism), adrenal fatigue, and low estrogen or progesterone can cause persistent exhaustion and brain fog.
4. Mood Swings and Anxiety
Hormonal fluctuations affect brain chemistry and emotional regulation. Women with hormonal imbalance may notice:
- Increased irritability
- Sudden mood swings
- Anxiety or panic attacks
- Low motivation or emotional sensitivity
Estrogen plays a key role in serotonin production (the “feel-good” chemical), so when it drops, mood changes can follow.
5. Sleep Problems
Hormones like melatonin, cortisol, and progesterone regulate sleep cycles. Imbalance can lead to:
- Difficulty falling asleep
- Frequent waking at night
- Restless sleep or insomnia
- Night sweats (often during perimenopause or menopause)
Quality sleep is essential for hormonal regulation, creating a cycle where poor sleep worsens hormonal imbalance.
6. Acne and Skin Changes
Hormonal acne is common, especially around the chin and jawline. It often appears as deep, cystic pimples that flare up around your menstrual cycle. Other skin symptoms include:
- Dry or oily skin
- Dark patches (melasma)
- Excess facial or body hair (hirsutism) due to high androgens
7. Hair Thinning or Hair Loss
Fluctuations in estrogen, progesterone, and thyroid hormones can cause noticeable hair shedding. Women may see thinning at the crown, widening of the hair part, or overall loss of hair volume.
8. Digestive Issues
Hormones influence gut motility and microbiome balance. Imbalance can lead to:
- Bloating
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Nausea
- Food cravings
Many women notice digestive changes during PMS or menopause, signaling the link between hormones and gut health.
9. Hot Flashes and Night Sweats
Sudden feelings of heat, flushing of the skin, and sweating — especially at night — are hallmark symptoms of declining estrogen levels, commonly experienced during perimenopause and menopause.
10. Low Libido
Decreased sexual desire or discomfort during intimacy can result from low estrogen, progesterone, or testosterone levels. Vaginal dryness and reduced natural lubrication are also common with hormonal changes.
11. Memory Issues and Brain Fog
Women with hormonal imbalance often report difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, and mental cloudiness. Estrogen helps protect brain function, so low levels can impair cognitive performance.
12. Breast Tenderness or Changes
Hormonal fluctuations can cause breast swelling, tenderness, or lumpiness, especially before periods. Persistent pain or unusual changes should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
When to See a Doctor
If you notice several of these symptoms affecting your quality of life, it’s best to consult a gynecologist, endocrinologist, or primary care doctor. Blood tests can measure hormone levels and identify any imbalances. Treatment may include lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, natural supplements, or hormone replacement therapy (HRT), depending on the cause.
Final Thoughts
Hormonal imbalance in women is common but often overlooked. Recognizing symptoms such as irregular periods, mood changes, weight fluctuations, sleep problems, and skin issues can help you take action early. With proper diagnosis and treatment, you can restore hormonal balance, boost energy, and improve overall health and well-being.